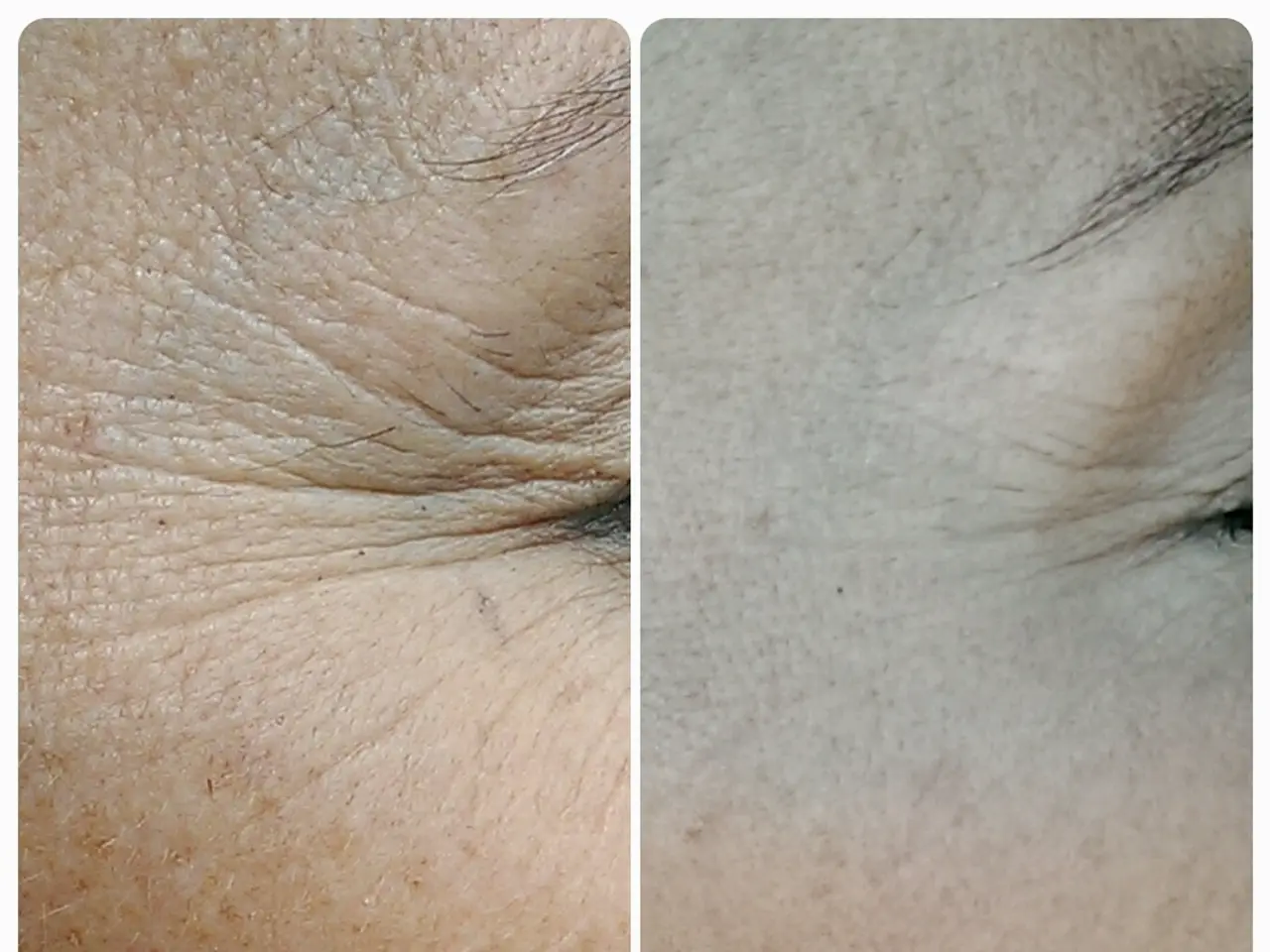
Top Essential Nutrients Combat Leading Cause of Early Aging
In the ongoing battle against skin aging, a host of natural antioxidants are proving to be valuable allies. These compounds, found in a variety of foods and plant extracts, provide broad-spectrum protection against UV damage and the processes collectively known as photoaging.
Green tea extract, when applied topically, protects against UVB rays and offers a layer of defense against skin aging. Lycopene, abundant in tomatoes and their products, provides long-term protection against skin erythema (sunburn). Thymoquinone, the key active ingredient in black cumin seed oil, supports the body against UV-induced ROS and reduces oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and mitochondrial dysfunction in keratinocytes, the main type of cell in the skin's outer layers [1].
Antioxidants such as polyphenols, grape seed extract, and astaxanthin combat photoaging and protect skin from UV damage primarily by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by UV radiation, thereby reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and subsequent skin damage [2]. Polyphenols, found abundantly in plants, act as potent ROS scavengers and have anti-inflammatory effects. For example, polyphenols in almonds provide UV protection and support skin moisture [3]. Grape seed extract is particularly rich in oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs) with about 50 times stronger antioxidant power than vitamin E, effectively reducing oxidative damage and inflammation in the skin [4]. Astaxanthin, a carotenoid antioxidant found in salmon, improves skin elasticity and hydration by protecting cellular components against UV-induced oxidative stress and supporting skin cell repair [2].
By mitigating oxidative damage, these antioxidants help maintain collagen and elastin integrity, reduce wrinkles and hyperpigmentation, and enhance overall skin health, thus slowing down photoaging and protecting against UV damage [1][3].
In addition to topical applications, certain micronutrients, when ingested, may provide an additional layer of protection from UV damage to the skin. Beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, is an antioxidant found in fruits, vegetables, salmon, eggs, and whole grains. Supplementation with beta-carotene may offer moderate protection against UV damage to the skin [5]. Lutein and zeaxanthin, found in green leafy vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, and cabbage, protect the skin against aging and damage by inhibiting cell loss, membrane damage, and elastin expression in UV-exposed fibroblasts [6].
However, it's important to note that while these antioxidants offer significant protection, they should not be relied upon as a replacement for sunscreen. Topical sunscreens provide a higher SPF, offering more immediate and direct protection against UVB rays. Antioxidants, when ingested or applied topically, provide an SPF that's lower but offer a secondary line of defense against the harmful effects of UV radiation.
References: [1] Mechanisms and therapeutic roles of medicinal plants in skin photoaging, DovePress, 2025 [2] GoodRx, The 10 Best Foods for Skin Health, 2025 [3] ISDIN Blog, What Are Free Radicals And How Do They Affect Skin?, 2025 [4] Helena Zhou Instagram post on Grape Seed Extract, 2025 [5] Mayo Clinic, Beta-carotene, 2025 [6] American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Lutein and Zeaxanthin Intake and Skin Aging, 2025
- In the realm of heart health and wellness, nutrition plays a crucial role, as certain antioxidants, such as those found in green tea extract, can support the body against UV-induced ROS and reduce oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
- For those with medical conditions or seeking to improve their overall fitness-and-exercise regimen, supplements like beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, may offer moderate protection against UV damage to the skin and support cardiovascular health.
- In the science of skin care, antioxidants like polyphenols, found abundantly in plants, act as potent ROS scavengers and have anti-inflammatory effects, supporting the maintenance of collagen and elastin integrity, and reducing wrinkles and hyperpigmentation.
- Wellness enthusiasts may also find value in consuming foods rich in antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, found in green leafy vegetables, which protect the skin against aging and damage by inhibiting cell loss, membrane damage, and elastin expression.
- In the pursuit of health-and-wellness, it's essential to remember that while antioxidants offer significant protection, they should not replace the use of medical-conditions like sunscreen, which provides a higher SPF, offering immediate and direct protection against UVB rays.